HPC
As part of the Parallel and High Performance Computing course, I implemented and analyzed parallel versions of a tsunami simulation based on the shallow water equations. Starting from a sequential C++ solver, I developed both MPI and CUDA implementations to accelerate the numerical computations.
The MPI version parallelized the time-step and solver routines, efficiently handling domain decomposition and ghost-row exchanges, achieving strong and weak scaling behaviors consistent with Amdahl’s and Gustafson’s laws.
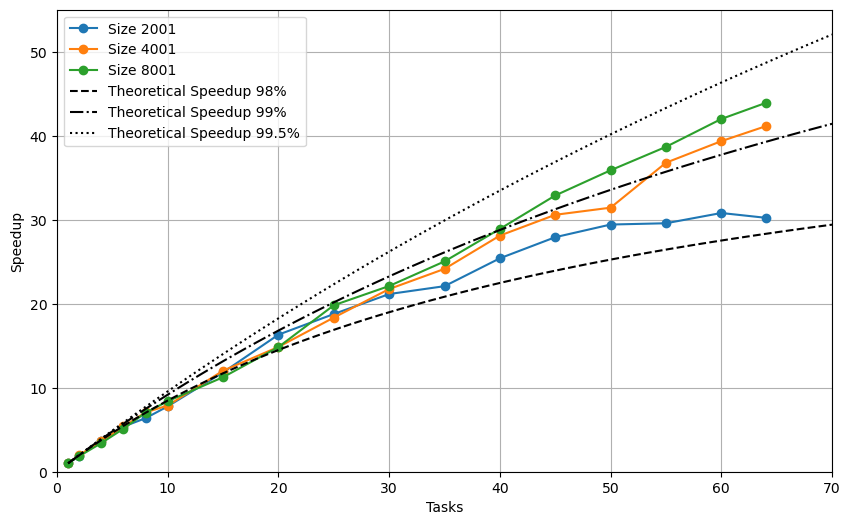
 Weak scaling results showing near-linear behavior with increasing tasks.
Weak scaling results showing near-linear behavior with increasing tasks.
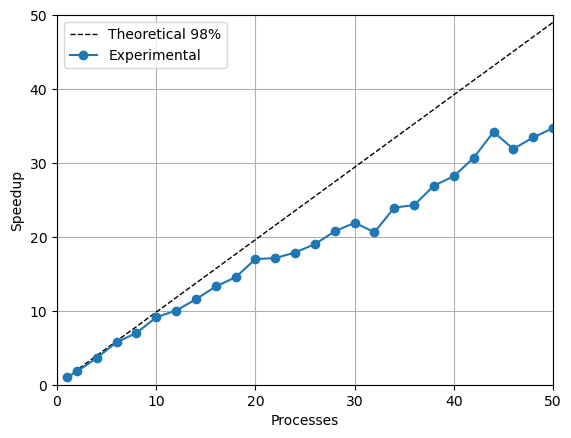
 Strong scaling results comparing experimental and theoretical speedup.
Strong scaling results comparing experimental and theoretical speedup.
The CUDA version introduced several optimized kernels for the solver, exploring the trade-off between workload distribution and hardware utilization through block- and grid-size tuning.
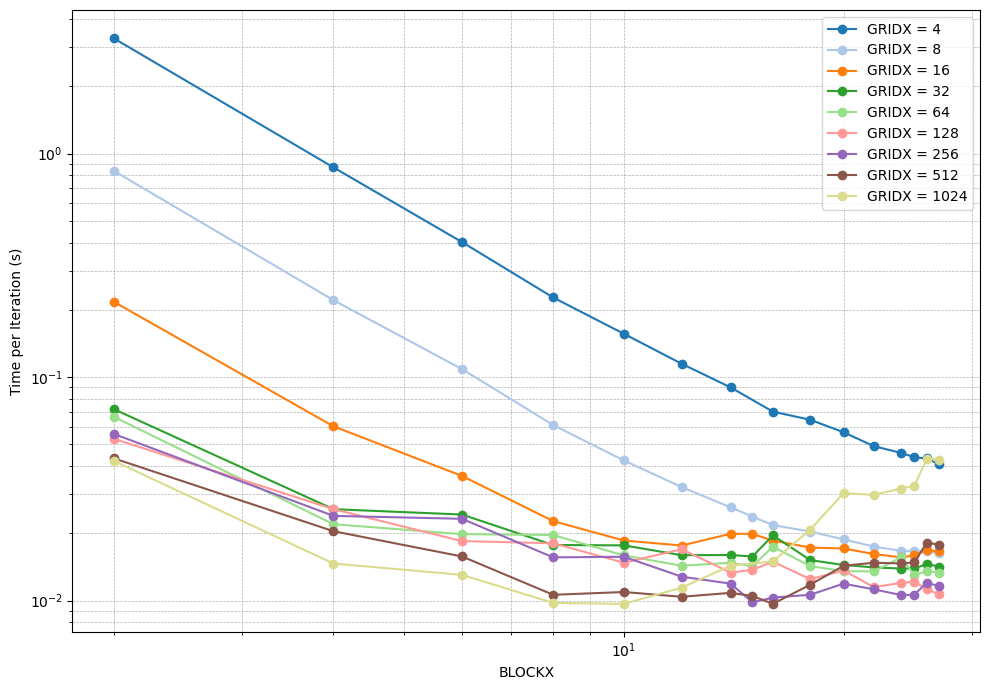 CUDA performance analysis showing time per iteration for different block and grid configurations.
CUDA performance analysis showing time per iteration for different block and grid configurations.
Overall, the parallelization led to significant speedups and scalability improvements, validating the efficiency of both CPU and GPU approaches.